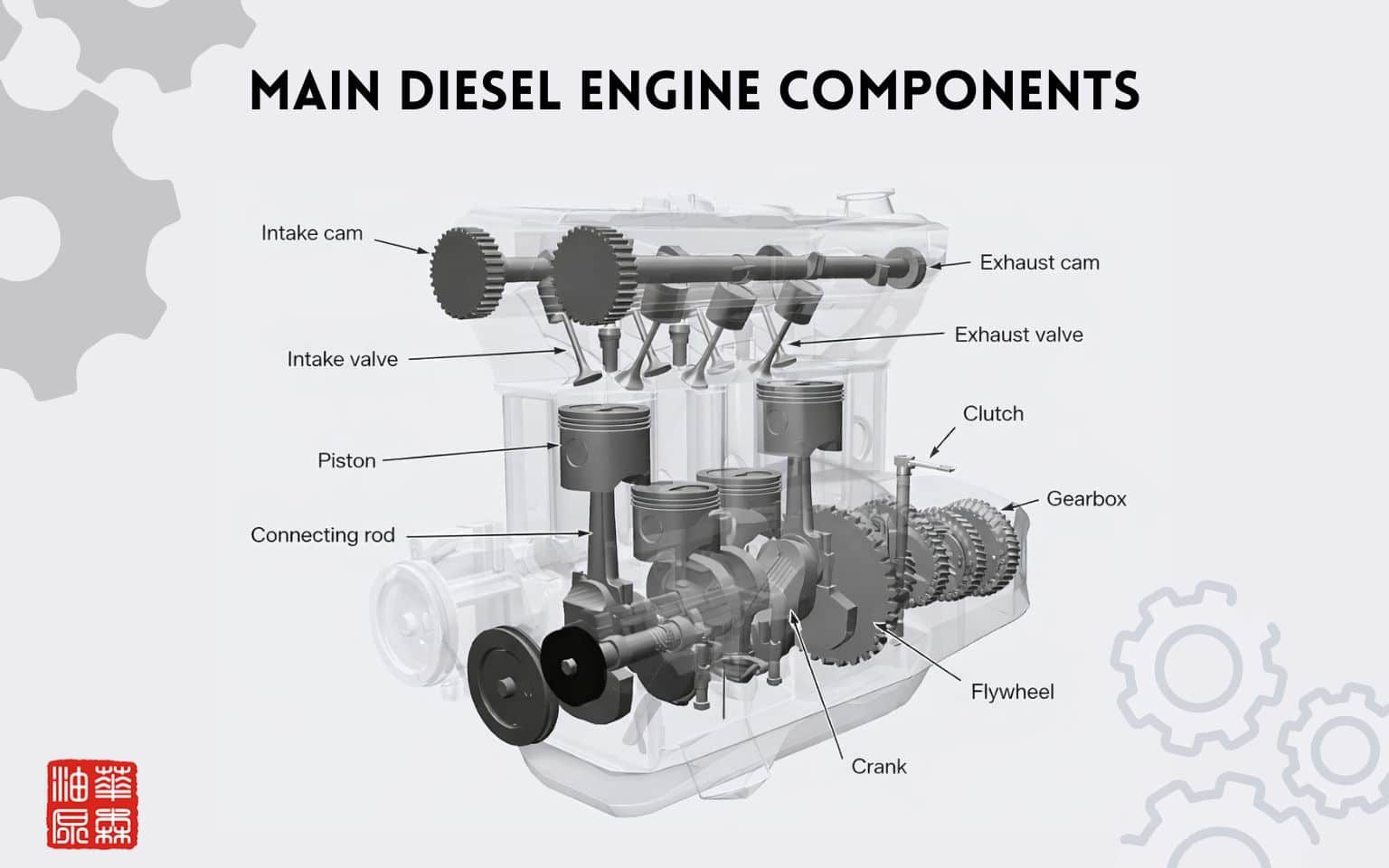
Main Diesel Engine Components and Their Functions
The main diesel engine components are the core parts that power heavy-duty vehicles and industrial machines used on roads and at work sites. Examples include trucks, buses, construction machines, and power generators. All of them rely on diesel engines because of their power, fuel-efficient, and long-lasting performance.
Understanding the main components help you to know how these machines generate power and why maintenance is important. Did you ever want to know what goes on under the hood when a diesel engine starts? This blog breaks it down step by step.
How Does a Diesel Engine Work?
First it is important to know how a diesel engine works? A diesel engine works on a simple principle, air is compressed to a high temperature inside the cylinder, and fuel is then injected into this heated air. The fuel ignites automatically due to the high temperature generated by compression, eliminating the need for a spark plug as required in petrol engines.
It follows a four-stroke cycle
- Intake Stroke – The piston moves down, drawing air into the cylinder.
- Compression Stroke – The piston moves up, compressing the air.
- Power Stroke – Fuel is injected, it ignites, and pushes the piston down.
- Exhaust Stroke – Burnt gases exit the cylinder.
Summary Table of Key Components
| Component | Function |
| Engine Block | Supports engine structure |
| Pistons | Compress air and transfer energy |
| Crankshaft | Converts motion to rotation |
| Fuel Injectors | Spray fuel for combustion |
| Turbocharger | Boosts air intake |
| Cooling System | Controls engine temperature |
Diesel Engine Mechanical Components
These parts form the structural and moving heart of the engine.
Engine Block
The engine block is the strong outer body of the engine. It is commonly made of cast iron or aluminum to handle high heat and pressure. The cylinders containing the fuel which burns to produce power are found inside the block.
You can think of it as the foundation of a home. All the other significant engine components are attached to it. Without a strong and properly positioned engine block, the entire engine cannot run effectively.
Cylinder Head
The cylinder head is mounted on the engine block. It also seals the end of the cylinders and makes the combustion chamber where fuel is burned. It carries important components of diesel engine such as valves and fuel injectors.
This component assists in regulating air flow in the air intake and the exhaust gas discharge. It is very important that there is a tight seal between the cylinder block and the head. If there is a leak, the engine could lose power.
Pistons and Piston Rings
Pistons are circular pieces of metal that move up and down in the cylinders. When the fuel is burned, the pressure forces the piston downward. It is the motion that generates the force required to operate the engine.
Piston rings are little metallic rings that are attached to the piston. They close the gap between the piston and the cylinder wall. This avoids leakage of air and fuel and ensures that the engine is efficient.
Crankshaft
The crankshaft converts the pistons’ up-and-down motion into rotational movement, which ultimately powers a vehicle’s wheels or drives heavy machinery. Without the crankshaft, the energy produced during combustion could not be used effectively. It continues to rotate as long as the engine is running and must be strong enough to stand up to very high levels of force and stress.
Connecting Rods
One end of the connecting rod is attached to the piston, and the other connects to the crankshaft. As the piston goes in and out, the connecting rod pushes the movement to the crankshaft.
They are manufactured in a way that they can handle a high level of pressure as they burn. Even a minor issue with a connecting rod can affect engine performance.
Valves and Valve Train
The valves regulate the air entry in the cylinder and discharge of exhaust gases after burning. Normally, there are inlet valves and outlet valves operating together.
The system which opens the valves at the right time is known as the valve train. It ensures that the valves are opened and closed in the ideal order of the movement of the piston. This is a very vital timing in smooth engine operation.
Fuel System Components
The fuel system is responsible for supplying diesel to the engine in the right quantity and at the right time. It is precise in its work as any slight variation in the pressure or time can influence performance. Properly functioning fuel systems ensure smooth combustion, better mileage, and longer engine life.
Fuel Tank and Lines
The diesel is also kept in the fuel tank until the time when the engine requires it. It is made in such a way that it avoids spillages and pollution.
Diesel is pumped in fuel lines to the engine. These lines have to be clean and free of wear which ensures uninterrupted flow of the fuel.
Fuel Filters
The diesel is first filtered with fuel filters before it is passed to delicate engine components. They eliminate dirt, dust which might exist in the fuel.
Clean fuel helps in preventing the wear of injectors and other parts. In case of a clogged filter, the engine will either lose power or it will not run smoothly.
Injection Pump
In the fuel system, the injection pump is important. It forces diesel to the injectors under high pressure.
This force is required due to the fact that diesel engines are dependent on the accuracy of fuel delivery. The timing of fuel injection is also regulated by the pump.
Injectors / Unit Injectors
The diesel is sprayed in a misty spray in the combustion chamber by injectors. This will enable the fuel to combine with compressed air well.
Enhanced fuel mixing translates to efficient burning, enhanced performance and enhanced fuel economy. Properly functioning injectors also contribute to the mitigation of the smokes and the emissions.
Air Intake and Exhaust Systems
Air is essential to an engine. It requires clean air which combines with fuel and generates power. Meanwhile, it should drive away the burnt gases safely and expeditiously.
The air intake and exhaust systems work together to keep the engine running smoothly. If airflow becomes restricted or blocked, the engine’s performance can decrease.
Air Filter
The first line of protection is the air filter. It prevents dust, dirt, and tiny particles from getting into the engine. Clean air assists in burning fuel by the engine. The contaminated air filter may lower the power and raise the fuel consumption.
Intake Manifold
Air passes from the filter into the intake manifold before entering the engine. It distributes the air to every cylinder. Even distribution of air is significant to balanced performance. When one cylinder receives less air, the engine will run rough.
Turbocharger
Turbocharger forces in additional air into the engine by means of exhaust gases. Having more air means that more fuel will be burnt to generate more power. This is used to improve the performance of heavy-duty engines without necessarily expanding the size of the engine. It also helps in saving fuel in a proper design.
Exhaust Manifold
Burned gases are collected by the exhaust manifold provided by the individual cylinders. It leads them to the exhaust system. The rapid elimination of emissions enables fresh air to get into the cylinders. This maintains the smooth running of the engine.
Lubrication and Cooling Systems
These systems protect the engine from wear and overheating.
Lubrication System
- Engine oil is circulated by the oil pump.
- The oil filter is used to remove impurities.
- Friction is decreased by the oil passages.
In the absence of lubrication, metal components would rub against one another.
Cooling System
- Coolant absorbs heat
- Radiator releases heat
- Coolant is circulated through the water pump.
- The thermostat controls temperature.
Think of it as the engine’s internal temperature control system.
Starting and Electrical Components
These parts allow the engine to start and operate efficiently.
Glow Plugs
Glow plug assists with the starting of the diesel engine during cold weather. The engine is activated after they have heated the air inside the combustion chamber.
Diesel engines also depend on high air temperature to start, therefore, cold air may complicate the starting. This issue is addressed by glow plugs which heat up the chamber so that fuel burns more easily.
Starter Motor and Battery
The battery provides the starter motor with electricity. When you switch the key or press the start button the starter motor starts rotating the engine. This rotation permits air compressed within the cylinders. After the engine gets started, the engine is self-contained.
Sensors and Control Units
Modern diesel engines have electronic control units commonly referred to as ECUs. Such mini computers are used to monitor real-time engine conditions.
They monitor temperature, time of fuel injection, airflow, and emission. Automatic adjustment of these factors makes the engine run more efficiently and emit a smaller quantity of pollutants.
Auxiliary and Optional Parts
Some additional components include:
- Flywheel
- Timing belt or timing chain
- Intercooler (in turbo engines)
- Emission control devices like EGR and DPF
These parts enhance performance, efficiency, and environmental compliance.
Final Thoughts
Understanding the main diesel engine components helps you see how an engine produces power and runs smoothly. Each part, such as the piston, crankshaft, connecting rod, and fuel system, plays an important role in performance and efficiency.
When these components of diesel engine work properly, the engine delivers reliable power and long service life. Learning about these parts also makes it easier to maintain the engine, detect problems early, and ensure better overall operation in vehicles and industrial machines.
FAQs
Q. What’s the difference between a diesel and petrol engine?
A. Diesel engines ignite fuel through compression, while petrol engines use spark plugs. Diesel engines are generally more fuel-efficient and durable.
Q. Why do diesel engines need glow plugs?
A. Glow plugs assist in cold starts by pre-heating the air inside the combustion chamber.
Q. How often should diesel engine components be serviced?
A. Most engines require regular oil changes every 5,000–10,000 km, but service intervals depend on manufacturer recommendations.
Q. What are the main parts of a diesel engine?
A. The main parts include the engine block, pistons, crankshaft, fuel system, air intake system, and cooling system.